The technique can be used to analyze the three primary financial statements, i.e., balance sheet, income statement, and cash flow statement. In the balance sheet, the common base item to which other line items are expressed is total assets, while in the income statement, it is total revenues. Vertical analysis makes financial statements comparable between companies of different sizes by converting line items into double declining balance depreciation method percentages of a base figure. For example, two retail firms may have vastly different revenue amounts, but expressing the costs of goods sold as a percentage of revenue shows which has a better cost structure.
Multi-year comparisons
Vertical analysis, often referred to as common-size analysis, is a crucial financial tool used in the world of business and finance to assess the relative proportions of different financial statement items. Vertical analysis looks at the contributing percentage of each line item to the total base figure. It can provide information on which metrics are improving and which are worsening.
- They let people compare different financial aspects in detail, helping make better decisions.
- By evaluating the proportions of various accounts over multiple periods, analysts can detect patterns in cost behavior, revenue composition, and asset utilization.
- One of the major benefits of vertical analysis is that it makes it simple to report to and communicate with stakeholders.
- The information provided in the balance sheet provides the change in working capital, fixed income over some time.
- Vertical analysis focuses on a single period, expressing each line item in percentages of total revenue or assets.
Conducting Vertical Analysis on Assets

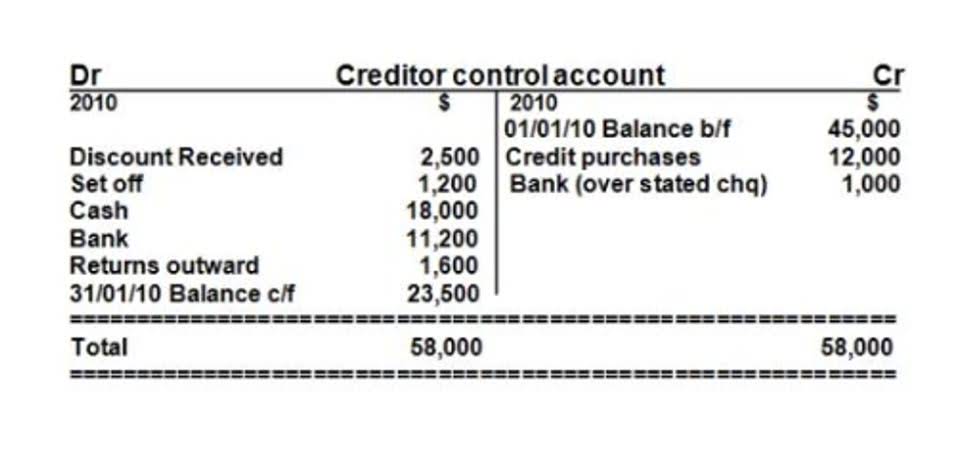
Vertical or proportional analysis refers to an accounting method where each line item in a financial statement is compared against another in the same statement. To perform a proportional analysis, each asset, liability, and equity item is divided by the total assets, then multiplied by 100 to get a percentage. The main components include the Income Statement, Balance Sheet, and Cash Flow Statement. Each of these statements provides crucial insights into different aspects of a company’s financial health.
Comparison
Much like ratio analysis, vertical analysis allows financial information of a small company to be compared with that of a large company. The common size percentage can also be used to compare different companies within the same industry or companies that use different currencies. Vertical analysis involves calculating percentages of line items based what is a vertical analysis? on a base figure for a period.
- For each line item, we’ll divide the amount by the corresponding period’s revenue to arrive at our contribution percentages.
- Vertical analysis, also known as common-size analysis, is a powerful tool used in finance to gain insights into the financial health and performance of a company.
- Vertical analysis relies on stable base figures, such as total revenue or total assets, which can vary significantly for companies in fluctuating industries.
- This analysis can uncover whether a company allocates an excessive portion of its revenue to certain costs, such as operating expenses or debt servicing, which can signal inefficiencies or financial risks.
- Most often, vertical analysis is used by management to find changes or variations in financial statement items of importance like individual asset accounts or asset groups.
- The following compares the performance of two companies using a vertical analysis on their income statements for 2019.
- To master techniques like vertical analysis, consider enrolling in finance courses.
That being said, there are some circumstances where cross comparing ratios of certain accounts would make sense. By doing both of these analyses, you can get an idea of how line items compare to themselves over time and whether those changes make sense in the context of the current time period as well. In this FAQ we will discuss what vertical analysis is, how it relates to horizontal analysis, and provide a simple example of how to apply it. accounting In our case, half of the company’s asset base comprises PP&E, with the rest coming from its current assets. Starting from the revenue line item, each line item on the income statement – if deemed appropriate – is divided by revenue (or the applicable core metric). Horizontal analysis indicates long-term trends and highlights areas of strength and those that need improvement.
- A 2019 McKinsey study found that top performing companies carefully manage the composition of expenses, keeping non-core costs below 15% of revenue.
- The primary benefit of vertical analysis is that it provides a clear picture of the relative size of each line item in a financial statement.
- Vertical analysis is a method used to evaluate the relative size of each line item on a financial statement.
- By converting complex financial data into percentages, it becomes more accessible for stakeholders to interpret and analyze.
- The primary components of financial statements include the income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement.
- For example, if long-term debt represents 40% of total assets, stakeholders can quickly gauge the company’s leverage and potential risk exposure.